 |
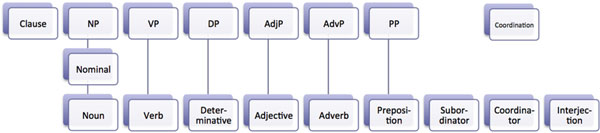
| The eight parts of speech are hiding in this diagram. (Wikipedia) |
Note: All right, class. Settle down. Today I want you to memorize--yes, memorize--the functions of the eight parts of speech. (Okay, not really, but you should be very familiar with them.)
Get Ready: Look at the picture above and find as many of the eight parts of speech as you can. (Hint: There are five.)
After learning of their benefits in Lesson #01-064, and seeing how flexible they are in Lesson #01-065, here, at last, are the long-awaited Eight Parts of Speech!
- Nouns: A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. This last category was added since I was in primary school. I guess someone noticed that "love" wasn't a thing! Barbers, Beijing, and butterflies are all nouns; so is beauty.
- Pronouns: A pronoun takes the place of a noun. "Mike said Mike is home, and Mike's family is fine." Yuck. "Mike said he's home, and his family is fine." Much better.
- Adjectives: Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, telling which, whose, what kind, and how many about the nouns and pronouns they modify. By the way, some of the smallest but scariest words in English are adjectives: a, an, and the. The little brown dog got to run free in the public park--lucky her!
- Verbs: A verb describes the action or condition of the subject (the main noun or pronoun) of the sentence. Action is easy to spot: eat, ate, eaten, eating. Condition is tougher; it's described by the "be" verbs (am, are, is, was, were, be, been, being) and also verbs like smell as in "The roses smelled good." The roses aren't doing any thing; they're just in a good-smelling state or condition.
- Adverbs: Adverbs are versatile. They may modify a verb, an adjective, or even another adverb. In this sentence, really modifies a verb: "He really ran." Here, it modifies an adjective: "He ran in a really big race." And here, another adverb: "He ran really fast."
- Conjunctions: A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses. The most common conjunctions are and, or, and but. Let's look at and joining words: "I like books and music." Now phrases: "I like to read books and listen to music." Finally, clauses: "I like to read books, and you like to listen to music."
- Prepositions: These words give English learners a lot of trouble. A preposition shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun (called "the object of the preposition") and a verb or other noun in a sentence. When I say, "The dog sat under the table," the preposition under shows the relationship of the noun table to the verb sat. It would be different (and weird!) if the dog sat on the table. As for a noun-to-noun relationship: "The vase with the flowers was knocked over." And now they're "the flowers on the floor"!
- Interjections: Finally, an interjection is a word that (usually) shows emotion, and has no grammatical relationship to the words around it, such as Wow! Oh? and Yes.
There you go! Being familiar with these will really help you improve your English.
--------Read more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/English_grammar#Word_classes_and_phrases
Practice: Name the part of speech of the underlined word.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
- Wow! Sheila and her dog were the very first customers in our café.
Answers are in the first comment below.
Submitted to the Shenzhen Daily for January 24, 2008


Answers to the Practice: 1. adjective; 2. verb; 3. conjunction; 4. noun; 5. adverb; 6. interjection; 7. pronoun; 8. preposition
ReplyDelete